In product development, understanding how the roof of the house of quality is used to analyze relationships is crucial for creating high-quality products. Many engineers and designers struggle to interpret this part of the Quality Function Deployment (QFD) matrix effectively. This guide explains its purpose, benefits, and practical application in a step-by-step manner.
What Is the Roof of the House of Quality?
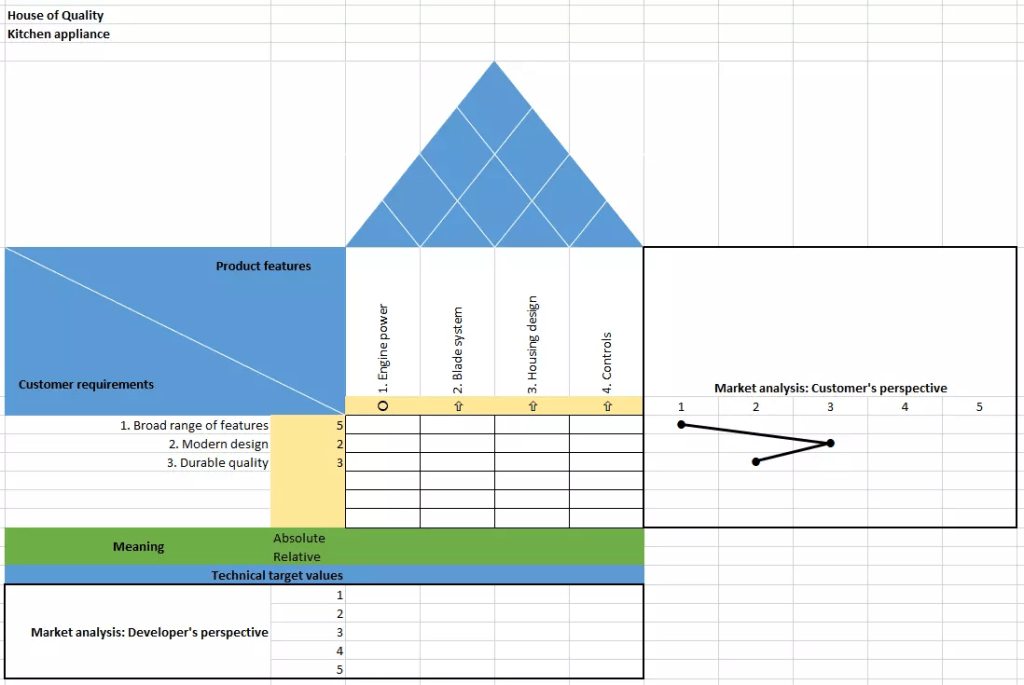
The roof of the house of quality is the triangular or peaked section at the top of a QFD matrix. It represents interrelationships between product characteristics or technical requirements.
Read too: Hail Damage Roof Repair: Essential Guide to Restoring Your Home’s Protection
Key points:
- Visually resembles a roof, hence the name.
- Shows correlations such as positive, negative, or neutral relationships.
- Helps engineers detect conflicts or synergies between technical features.
According to the American Society for Quality, properly analyzing the roof can prevent design conflicts and optimize product functionality.
Purpose of the Roof in QFD
- Identify Conflicting Features
- Detects when one technical requirement may negatively impact another.
- Highlight Synergies
- Reveals areas where improving one feature positively supports others.
- Facilitate Decision Making
- Guides prioritization of technical improvements based on interdependencies.
- Improve Overall Product Quality
- Ensures that all product characteristics are aligned with customer needs.
How to Read the Roof of the House of Quality
| Symbol | Meaning |
|---|---|
| ▲ | Strong positive correlation |
| ○ | Moderate correlation |
| ▼ | Negative correlation |
| Blank | No significant relationship |
- Rows and columns of the roof correspond to technical requirements.
- Cross-referencing cells indicates how changes in one feature affect another.
- Designers use this data to balance performance, cost, and manufacturability.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using the Roof in QFD
1. List Technical Requirements
- Collect all key product specifications.
- Ensure they are measurable and actionable.
2. Draw the Roof Structure
- Create a triangular section at the top of the QFD matrix.
- Align rows and columns with the technical requirements.
3. Assess Interrelationships
- Evaluate each intersection using symbols (▲, ○, ▼).
- Consider engineering data, simulations, or past product performance.
4. Analyze Conflicts and Synergies
- Identify which features may create trade-offs.
- Use this insight to adjust design priorities.
5. Integrate With Customer Needs
- Connect roof insights to the main body of the house of quality.
- Ensure technical improvements support the voice of the customer.
Benefits of Using the Roof of the House of Quality
- Improved Product Design: Prevents conflicts before production.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Aligns engineering, design, and marketing teams.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces costly redesigns by identifying problem areas early.
- Customer Satisfaction: Ensures technical decisions enhance perceived value.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Ignoring negative correlations, which can cause design conflicts.
- Overcomplicating the roof with too many technical requirements.
- Failing to update the roof when requirements change during development.
- Relying solely on subjective judgment without supporting data.
FAQ – The Roof Of The House Of Quality Is Used To
1. Why is it called the “roof” of the house of quality?
Because its triangular shape at the top of the QFD matrix resembles a house roof.
2. Can the roof show conflicts between product features?
Yes, negative correlations indicate features that may conflict with each other.
3. How do I prioritize technical requirements using the roof?
Focus on requirements that have strong positive synergies and minimal conflicts.
4. Is the roof applicable for all types of products?
Yes, it’s a versatile tool in QFD applicable to both tangible and digital products.
5. How often should the roof be updated?
Update whenever technical requirements or customer needs change during development.
6. Can software tools help with the roof analysis?
Yes, QFD software like QFD Capture or Excel templates can simplify roof calculations.
Conclusion
The roof of the house of quality is used to visualize relationships between technical requirements, detect conflicts, and optimize product design. By carefully analyzing the roof, teams can make informed decisions, reduce design risks, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Share this guide with colleagues or fellow engineers to improve your next product development project using the house of quality framework.



Leave a Reply