Understanding what are the parts of a roof in a house is essential for homeowners, DIY enthusiasts, or anyone planning home improvement. A well-constructed roof not only protects your home from weather but also contributes to energy efficiency and overall safety. This guide breaks down each component, its purpose, and maintenance tips in an easy-to-understand way.
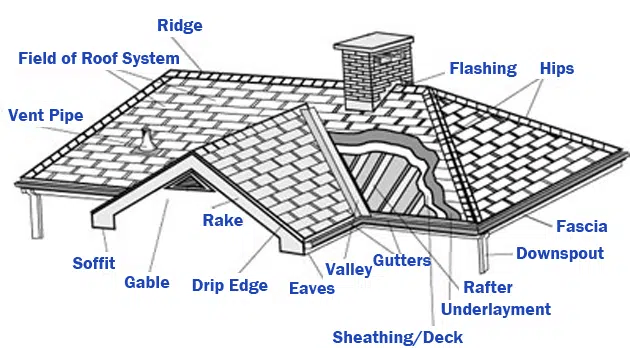
Main Parts of a Roof
A house roof consists of several key components working together to provide stability, protection, and insulation.
Read too: Is It Reasonable to Ask the Seller to Replace the Roof?
1. Ridge
The ridge is the horizontal peak where two sloping roof planes meet. It’s usually capped with ridge shingles to prevent water penetration and ensure a finished look.
2. Rafters and Trusses
- Rafters: Sloped beams that support the roof deck.
- Trusses: Pre-fabricated triangular units that provide structural support.
Together, these elements form the skeleton of your roof.
3. Roof Decking or Sheathing
The decking is the flat layer of plywood or OSB attached to rafters/trusses. It serves as the base for underlayment and shingles.
4. Underlayment
A protective layer (felt or synthetic) installed over the decking to provide waterproofing and extra protection against wind-driven rain.
5. Roof Covering
The roof covering is the visible layer that shields the home from the elements. Common materials include:
- Asphalt shingles
- Metal panels
- Clay or concrete tiles
- Wood shakes
6. Eaves and Soffits
- Eaves: The lower edge of the roof that overhangs walls, directing water away.
- Soffits: The undersides of eaves, often vented to allow airflow into the attic.
7. Fascia
A board along the edge of the roof that supports gutters and finishes the edge aesthetically.
8. Flashing
Metal strips installed at joints, valleys, and around chimneys/vents to prevent water leaks.
9. Gutters and Downspouts
Channels rainwater from the roof to the ground, protecting the foundation and siding from water damage.
Roof Types and Their Components
| Roof Type | Key Features | Common Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Gable Roof | Two sloping sides forming a triangle | Asphalt, Metal, Shingles |
| Hip Roof | Slopes on all four sides | Asphalt, Tile, Wood |
| Flat Roof | Minimal slope for drainage | TPO, EPDM, Built-up Felt |
| Mansard Roof | Double slope on all sides | Slate, Asphalt, Tile |
| Gambrel Roof | Steep lower slope, shallow upper slope | Wood Shingles, Metal |
Insight: Each roof type shares common components like decking, underlayment, and flashing but differs in structural design and slope.
Step-by-Step Roof Maintenance Tips
- Inspect shingles and tiles for cracks or displacement.
- Clean gutters and downspouts regularly to prevent water buildup.
- Check flashing around chimneys, vents, and valleys for rust or gaps.
- Ensure soffit vents are unobstructed for proper attic ventilation.
- Remove debris such as leaves or branches to prevent moisture retention.
Pro Tip: Conduct inspections twice a year—spring and fall—for optimal roof longevity.
Common Roof Problems and How to Identify Them
- Leaks: Often caused by damaged flashing, missing shingles, or clogged gutters.
- Sagging: Indicates weakened trusses, decking, or water damage.
- Curling or Cracked Shingles: Usually due to age, poor installation, or extreme weather.
- Ice Dams: Form when heat escapes from the attic, melting snow that refreezes at the eaves.
FAQ Section
Q1: What is the difference between rafters and trusses?
A1: Rafters are individual beams supporting the roof deck, while trusses are pre-fabricated triangular structures providing overall support.
Q2: How long does a typical roof last?
A2: Lifespan depends on material—Asphalt shingles last 20–30 years, metal 40–70 years, clay tiles 50–100 years.
Q3: Do all roofs need gutters?
A3: While not mandatory, gutters protect the foundation, siding, and landscaping from water damage.
Q4: Can I replace a single part of the roof or do I need a full replacement?
A4: Minor issues like damaged shingles or flashing can be repaired individually. Full replacement is only necessary when structural components or multiple layers are compromised.
Q5: What is the function of soffits and fascia?
A5: Soffits allow attic ventilation, reducing moisture buildup. Fascia supports gutters and provides a clean roof edge finish.
Conclusion
Knowing what are the parts of a roof in a house helps homeowners maintain, inspect, and repair their roofs efficiently. From structural elements like rafters and trusses to protective layers like shingles and flashing, every part contributes to the roof’s durability and the home’s safety.
Share this guide with friends or family to help them better understand their roof’s structure and maintenance needs!


Leave a Reply