If you’ve ever noticed the section of your roof that extends past the exterior walls, you might have wondered what it’s called and why it matters. Many homeowners search for part of the roof that hangs over the house because this feature plays a major role in protection, comfort, and curb appeal. In this guide, we’ll clearly explain what this roof section is, what it does, and why it’s so important for your home.
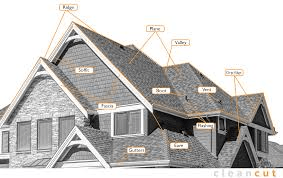
Part Of The Roof That Hangs Over The House: What Is It Called?
The part of the roof that hangs over the house is most commonly called the eaves.
In simple terms, eaves are the edges of the roof that extend beyond the exterior walls of a building. They are found on most residential homes and serve both functional and aesthetic purposes.
Read too: Hail Damage Roof Repair: Essential Guide to Restoring Your Home’s Protection
What Are Eaves? (Simple Definition)
Eaves are the lower edges of a roof that project outward beyond the house walls. This projection is known as a roof overhang.
Basic Characteristics of Eaves
- Located at the roof’s perimeter
- Extend horizontally beyond walls
- Often include soffit and fascia components
For general background on roof eaves and roof edges, see this neutral reference on Wikipedia:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eaves
Why Do Roofs Have Overhangs in the First Place?
Roof overhangs are not just decorative. They solve several real-world problems.
Main Purposes of Roof Overhangs
- Protect walls from rain and moisture
- Provide shade and reduce heat gain
- Prevent water from entering windows and doors
- Improve ventilation and airflow
- Enhance architectural balance
Building Insight: Homes with properly sized eaves tend to experience fewer moisture-related issues over time.
Main Parts of the Roof Overhang
The part of the roof that hangs over the house is made up of several components working together.
1. Eaves
The overall overhanging section of the roof.
2. Soffit
The underside of the roof overhang.
Functions of soffit:
- Covers exposed rafters
- Allows attic ventilation
- Prevents pests from entering
3. Fascia
The vertical board at the edge of the roof.
Functions of fascia:
- Supports gutters
- Gives the roof a finished appearance
- Protects roof edges
Together, eaves, soffit, and fascia form the complete roof overhang system.
Different Types of Roof Overhangs
Not all roof overhangs are the same. Their design varies by architecture and climate.
1. Open Eaves
- Exposed rafters
- Common in rustic or craftsman homes
- More maintenance required
2. Closed (Boxed) Eaves
- Enclosed soffit underneath
- Cleaner, more modern appearance
- Better pest and moisture protection
3. Wide Overhangs
- Extend 24 inches or more
- Excellent sun and rain protection
- Common in tropical and farmhouse designs
4. Narrow Overhangs
- Minimal extension
- Modern aesthetic
- Less weather protection
How Roof Overhangs Protect Your Home
Rain Protection
Eaves direct rainwater away from:
- Exterior walls
- Windows and doors
- Foundation
This reduces the risk of:
- Wood rot
- Mold growth
- Water intrusion
Sun and Heat Control
Overhangs block high-angle summer sun while allowing lower winter sun to enter.
Result:
- Cooler indoor temperatures
- Lower air conditioning costs
Do Roof Overhangs Improve Energy Efficiency?
Yes—especially in warm and mixed climates.
Energy Benefits
- Reduced solar heat gain
- Lower attic temperatures
- Improved HVAC efficiency
Energy Insight: When combined with insulation and ventilation, roof overhangs can noticeably reduce cooling loads.
Roof Overhangs and Climate: Why Size Matters
Hot Climates
- Wide eaves provide shade
- Protect walls from UV damage
Rainy Climates
- Longer overhangs reduce wall saturation
- Help prevent foundation erosion
Cold Climates
- Overhangs help manage snow melt
- Prevent ice buildup near walls
Choosing the right overhang size is critical for long-term performance.
Common Roof Styles and Their Overhangs
| Roof Style | Typical Overhang |
|---|---|
| Gable Roof | Moderate eaves |
| Hip Roof | Even eaves on all sides |
| Flat Roof | Minimal or none |
| Shed Roof | Single-direction overhang |
| Craftsman | Deep, decorative eaves |
Each roof style uses overhangs differently to match structure and design goals.
How Far Should a Roof Overhang Extend?
There is no one-size-fits-all answer.
Typical Roof Overhang Sizes
- 12 inches – standard protection
- 18–24 inches – enhanced shade and rain control
- 30+ inches – deep porches or architectural designs
Factors That Affect Overhang Size
- Climate
- Roof pitch
- Wall height
- Local building codes
Builder Tip: Overhangs that are too short may offer little protection, while overly large overhangs require additional structural support.
Common Problems When Roof Overhangs Are Missing or Damaged
Without Proper Overhangs
- Water stains on siding
- Premature paint failure
- Higher indoor temperatures
- Increased maintenance costs
Damaged Overhangs Can Cause
- Rotting fascia boards
- Sagging soffits
- Pest infestations
- Gutter failure
Regular inspection helps prevent costly repairs.
Step-by-Step: How to Inspect Your Roof Overhang
Step 1: Visual Check
Look for cracks, sagging, or peeling paint.
Step 2: Check Soffit Vents
Ensure vents are clear and unobstructed.
Step 3: Inspect Fascia
Check for soft spots or rot.
Step 4: Look for Pests
Bird nests or insects indicate gaps.
Step 5: Examine Gutters
Loose gutters can damage fascia over time.
Roof Overhangs vs Gutters: What’s the Difference?
Many people confuse the two.
| Feature | Roof Overhang | Gutter |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Protection & shade | Water collection |
| Location | Roof edge | Mounted to fascia |
| Always present? | Often | Optional |
Both work together to manage rainwater effectively.
Do All Houses Have Roof Overhangs?
No.
Homes Without Overhangs
- Some modern designs
- Flat-roof structures
- Minimalist architecture
These homes rely heavily on:
- Advanced waterproofing
- High-quality siding
- Proper drainage systems
Can Roof Overhangs Be Added or Extended?
Yes, but it’s not always simple.
When Extension Makes Sense
- Frequent wall moisture issues
- Excessive sun exposure
- Siding deterioration
Considerations
- Structural support
- Roof redesign
- Permit requirements
- Cost vs benefit
Professional evaluation is strongly recommended.
Cost Considerations
New Construction
- Overhang cost is integrated into design
- Relatively low added cost
Retrofit or Extension
- Moderate to high cost
- Structural modifications required
Value Insight: Proper overhangs often save money long-term by reducing repairs and energy use.
FAQ – Part Of The Roof That Hangs Over The House
Q1: What is the part of the roof that hangs over the house called?
It is called the eaves, also known as a roof overhang.
Q2: Are eaves necessary on a house?
They are not mandatory, but they provide significant protection and energy benefits.
Q3: What’s the difference between eaves and soffit?
Eaves are the entire overhang, while the soffit is the underside of that overhang.
Q4: Can roof overhangs prevent water damage?
Yes. They help keep rain away from walls, doors, and foundations.
Q5: Do modern homes still use roof overhangs?
Yes, though designs may use smaller or concealed overhangs.
Conclusion
The part of the roof that hangs over the house—known as the eaves—is one of the most important yet overlooked elements of residential design. From protecting your walls and foundation to improving comfort and energy efficiency, roof overhangs play a vital role in your home’s performance and appearance. Understanding how they work helps you maintain, design, or upgrade your home more confidently. If this guide clarified things for you, share it on social media so others can better understand the importance of roof overhangs too.

Leave a Reply