When it comes to roofing options, metal roofs are often praised for their durability, energy efficiency, and modern aesthetic. However, one common concern among homeowners is whether metal roofs attract lightning more than other types of roofing materials. In this article, we will delve into the question, “Do metal roofs attract lightning?” and uncover the facts behind this intriguing topic.
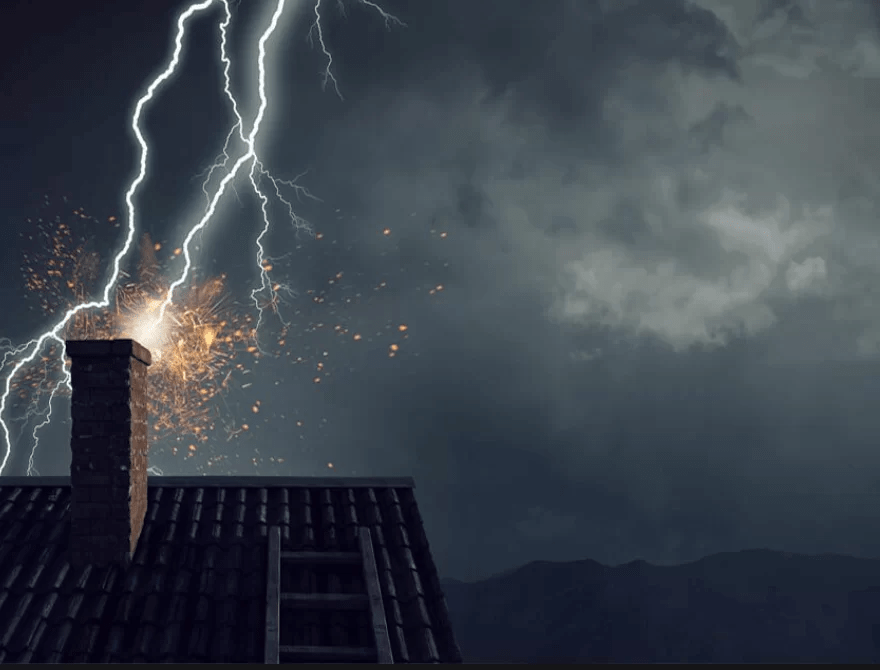

Understanding Lightning and Roof Materials
Before addressing whether metal roofs attract lightning, it is important to understand how lightning works and how different materials interact with it. Lightning is a powerful electrical discharge that occurs when there is a buildup of electrical charge between the atmosphere and the ground. This discharge seeks the shortest path to the ground, which often involves objects or structures that are high and conductive.
The Conductivity of Metal Roofs
Metal roofs are known for their conductivity, which means they can efficiently conduct electricity. However, this characteristic alone does not necessarily mean that metal roofs are more likely to attract lightning. In fact, the material of the roof is just one factor among many that influence lightning strikes.
Read too: Is It Reasonable to Ask the Seller to Replace the Roof?
Do Metal Roofs Attract Lightning?
When considering whether metal roofs attract lightning, it’s crucial to differentiate between attraction and conduction. Metal roofs do not attract lightning any more than other materials. Instead, they are highly effective at safely conducting electrical charges to the ground if a lightning strike occurs.
The Myth of Lightning Attraction
The idea that metal roofs attract lightning is a common myth. Lightning is primarily attracted to tall structures and objects that are good conductors of electricity. Since metal roofs are generally installed on top of buildings, they are not necessarily more attractive to lightning than other roofing materials. Rather, the height and prominence of the building itself are more significant factors in determining where lightning will strike.
Metal Roofs and Safety Measures
One of the advantages of metal roofs in terms of lightning safety is their ability to conduct electricity away from the structure. When lightning strikes a metal roof, the electrical charge is distributed evenly across the surface and safely redirected to the ground through the building’s grounding system. This reduces the risk of electrical fires and other hazards associated with lightning strikes.
Lightning Protection Systems
For added safety, many buildings with metal roofs are equipped with lightning protection systems. These systems typically include lightning rods or air terminals, which are installed to provide a direct path for lightning to reach the ground safely. By incorporating such systems, homeowners can further minimize the risks associated with lightning strikes.
Comparing Metal Roofs with Other Roofing Materials
To understand the role of metal roofs in lightning safety, it’s helpful to compare them with other common roofing materials.
Asphalt Shingles
Asphalt shingles are one of the most widely used roofing materials. Unlike metal roofs, asphalt shingles are not conductive. However, this does not necessarily make them safer or more resistant to lightning strikes. In fact, the presence of a metal framework or other conductive materials in the building’s structure can still pose a risk.
Clay and Concrete Tiles
Clay and concrete tiles are another popular choice for roofing. These materials are non-conductive and offer their own set of advantages and disadvantages. While they are not likely to attract lightning, they can still be vulnerable to damage from a lightning strike if the building’s overall lightning protection system is inadequate.
The Role of Building Height and Location
The likelihood of lightning striking a building is influenced by factors such as its height and location. Taller buildings and structures that are isolated or situated on elevated ground are more likely to be struck by lightning. This is true regardless of the roofing material used.
Building Height
A taller building is more likely to be struck by lightning simply because it is closer to the electrical discharge in the atmosphere. This increased risk is independent of whether the building has a metal roof or another type of roofing material.
Geographic Location
The geographic location of a building also plays a significant role in lightning strikes. Areas with frequent thunderstorms or high lightning activity will experience more lightning strikes overall. In such regions, the choice of roofing material, including metal, will have minimal impact on the likelihood of being struck.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways
To summarize, metal roofs do not attract lightning more than other types of roofing materials. Instead, their conductive properties help to safely redirect electrical charges to the ground, reducing the risk of electrical fires and other hazards. The height and location of a building are more influential factors in determining the likelihood of lightning strikes. For added protection, consider installing a lightning protection system to ensure safety during thunderstorms.


Leave a Reply