As homeowners seek ways to improve their living space, one renovation project that often comes to mind is raising the roof. If you’ve ever wondered, “How do you raise the roof on an existing house?” you’re not alone. This ambitious yet rewarding project allows you to expand your attic space, improve headroom in rooms with sloped ceilings, or even create a whole new level for living space.
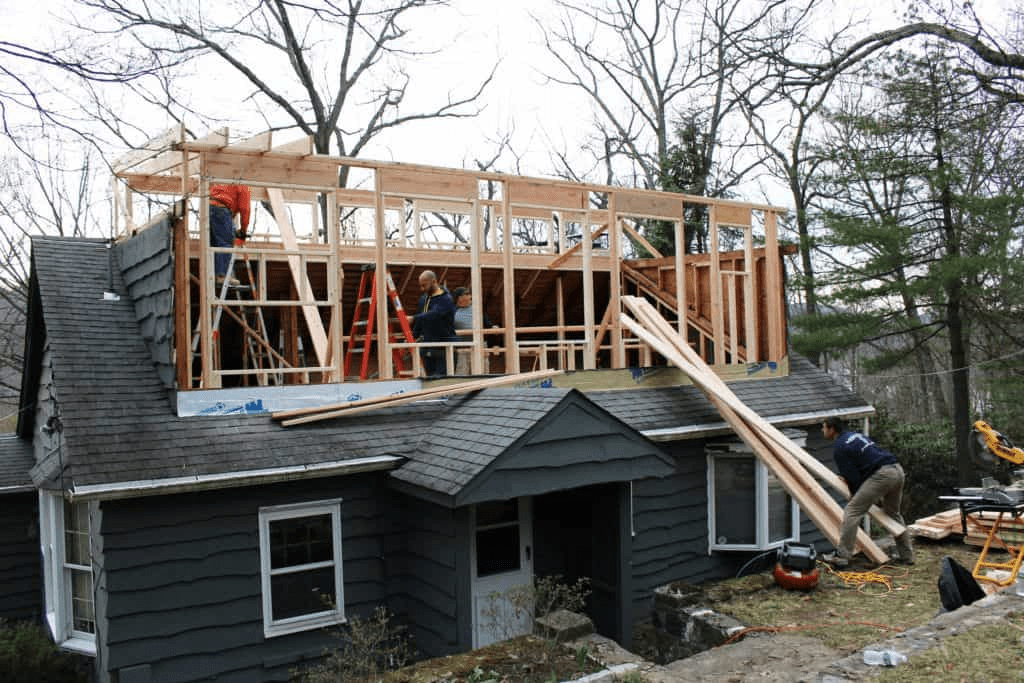

Raising the roof on an existing house is a significant home improvement task that requires careful planning, professional expertise, and a good understanding of building codes and structural requirements. In this article, we will explore everything you need to know about raising the roof of your home, from the initial planning stages to the completion of the project.
Read too: How Long Do Standing Seam Metal Roofs Last? A Comprehensive Guide to Durability and Longevity
Why Would You Want to Raise the Roof?
Before diving into the “how-to” of raising a roof, let’s first consider why you might want to undertake such a project. There are several compelling reasons to raise the roof on an existing house, including:
- Creating More Space: If your current ceiling is low or the attic is cramped, raising the roof can provide more headroom and create additional space for storage or even living space.
- Adding a Second Story: For homes that have limited space, raising the roof might be the key to adding a second floor. This can significantly increase the value of your home by expanding its usable square footage.
- Improving Natural Light and Ventilation: A higher roof can open up opportunities to install larger windows or skylights, which can improve natural lighting and ventilation.
- Enhancing the Aesthetic Appeal: In some cases, raising the roof may be done purely for aesthetic reasons, to achieve a more modern or open feel in the home.
How Do You Raise The Roof On An Existing House?
Now that we understand why someone might want to raise the roof, let’s explore how to go about it. Raising the roof is not a DIY project for most homeowners due to its complexity, but with the right planning and professional help, it can be done successfully.
Step 1: Assess the Structure of Your Home
Before making any changes, it’s essential to assess whether your house can support the structural modifications needed for a raised roof. This requires a structural engineer or an architect to evaluate the current load-bearing walls, roof structure, and overall integrity of the home.
- Check for Load-Bearing Walls: You’ll need to identify which walls are load-bearing. These are the walls that support the weight of the roof and the upper levels of the house.
- Evaluate Roof Framing: The existing roof framing must also be assessed to determine if it can handle the changes that will occur when the roof is raised.
- Plan for Reinforcement: In many cases, additional reinforcement may be required for the home’s foundation or walls to support the new roof height.
Step 2: Obtain Necessary Permits
Before beginning any work, it is crucial to obtain the necessary permits from your local building authority. Raising the roof involves significant structural changes to your home, which means that inspections and permits are required to ensure compliance with building codes.
- Building Permits: These are typically required for any major structural modifications to a home.
- Zoning Permits: Check with your local zoning office to ensure that raising the roof is permitted under local zoning laws. There may be height restrictions or other guidelines that you need to follow.
- Historic Preservation Permits: If your home is in a historic district, you may need additional approval before making structural changes.
Step 3: Create a Design Plan
Once you’ve assessed the feasibility of raising the roof and obtained the necessary permits, it’s time to work with an architect or designer to create a design plan. This plan should detail:
- Roof Design: Whether you plan to raise the roof straight up or make modifications to the roofline (such as adding dormers or gables).
- New Structure: If you’re planning to add another floor or extend the attic, the design should include new framing, supports, and other structural components.
- Roof Pitch: Consider whether you want a steeper roof pitch or a more gradual slope. This will impact both the aesthetic appeal and functionality of the space.
Step 4: Hire a Qualified Contractor
Raising the roof is not something that can be done with just a few tools and a weekend’s worth of work. It requires professional expertise, especially when it comes to structural integrity, roofing, and foundation work.
- General Contractor: A general contractor will help manage the project and coordinate with the necessary subcontractors, such as framers, roofers, and electricians.
- Specialized Roofing Contractors: It’s essential to hire a contractor with experience in roof raising or remodeling. This type of work requires specialized knowledge of roofing systems and how to modify them without compromising the structure.
- Structural Engineer: A structural engineer will help ensure that the house can support the new roof height and provide guidance on reinforcing walls, beams, and other structural elements.
Step 5: Begin the Roof Raising Process
Once the plan is in place and contractors are hired, the process of raising the roof begins. Here’s what to expect:
- Removing the Existing Roof: The first step is to carefully remove the existing roof, which may involve removing shingles, roofing materials, and roof framing. Depending on the extent of the roof raising, this could include taking down walls and removing parts of the ceiling.
- Reinforcing the Structure: As the old roof is removed, contractors will reinforce the walls, foundation, and support beams to accommodate the new roof height. This may include adding additional framing, beams, or columns to provide extra support.
- Raising the Roof Structure: The process of actually raising the roof may involve lifting the entire roof structure, adding more height to the frame, and then rebuilding the roof. The roof trusses may be modified, or new trusses may be added to match the new height.
- Installing New Roof Framing: Once the structure is raised, new roof framing will be installed. This may include additional beams, ridge boards, and support columns to ensure that the new roof is stable.
- New Roofing Materials: After the framing is in place, new roofing materials—whether metal, shingles, or another option—are installed. This may require special considerations based on the new pitch of the roof.
Step 6: Finish Interior and Exterior Work
After the roof itself is raised, there will still be several steps left to complete the project:
- Interior Work: You may need to install new insulation, drywall, or flooring in the newly created space. If you’ve added a second story, rooms will need to be framed and finished.
- Exterior Work: The exterior of the house will also need to be adjusted. This could include modifying gutters, windows, and siding to match the new roof height and design.
- Final Inspections: Before you can move in, the project must undergo a final inspection by local authorities to ensure everything complies with building codes.
How Do You Raise The Roof On An Existing House? The Final Thoughts
Raising the roof on an existing house is a major undertaking that requires careful planning, professional help, and attention to detail. However, with the right preparation, this renovation can provide more living space, improve the home’s aesthetic appeal, and even increase its value. If you’re asking, “How do you raise the roof on an existing house?” this guide should give you a solid understanding of the steps involved, from assessment and permits to construction and final touches.

Leave a Reply