Pre-engineered metal buildings (PEMBs) have gained popularity in recent years due to their versatility, durability, and cost-effectiveness. One critical aspect of these structures is their roofing system. Understanding Pre Engineered Metal Building Roof Details is crucial for ensuring the longevity and performance of your building. This article delves into the intricacies of PEMB roofs, offering valuable information for architects, builders, and property owners.
The Basics of Pre Engineered Metal Buildings
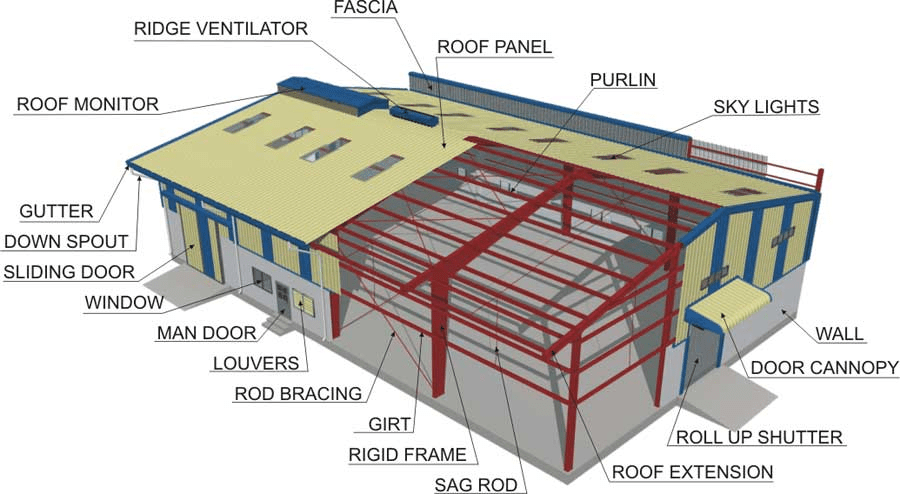
Before we delve into the specifics of the roof, it’s important to understand what constitutes a pre-engineered metal building. PEMBs are constructed using a prefabricated steel framework, which is then assembled on-site. These buildings are commonly used for warehouses, industrial facilities, commercial spaces, and even residential applications due to their efficiency and adaptability.
Read too: Decoding Timelines: How Long Does It Take To Replace A Roof and What to Expect
Why Focus on Roof Details?
The roof is a vital component of any building, providing protection from the elements and contributing to the overall structural integrity. In PEMBs, the roof must be designed and installed correctly to ensure it performs well over its lifespan. Detailed attention to roof design, materials, and construction techniques can prevent issues such as leaks, structural failures, and energy inefficiency.
Key Components of Pre Engineered Metal Building Roofs
Understanding the key components of PEMB roofs is essential for anyone involved in the design or construction process. Here are the main elements:
1. Roof Panels
Roof panels in PEMBs are typically made from high-quality steel and come in various profiles and thicknesses. The choice of panels depends on factors such as climate, building use, and aesthetic preferences.
2. Purlins
Purlins are horizontal beams that support the roof panels. They play a critical role in distributing the load from the roof to the primary structural frame. Proper spacing and alignment of purlins are crucial for maintaining the roof’s structural integrity.
3. Insulation
Insulation is essential for regulating the temperature inside the building and preventing condensation. Various insulation materials can be used, including fiberglass, foam, and reflective insulation.
4. Fasteners
Fasteners secure the roof panels to the purlins and the overall structure. High-quality fasteners that are resistant to corrosion are necessary to ensure the longevity of the roof.
5. Flashing and Trim
Flashing and trim are used to seal edges, joints, and penetrations in the roof. They prevent water infiltration and enhance the roof’s aesthetic appeal.
Pre Engineered Metal Building Roof Details
Roof Panel Selection
Choosing the right roof panel is a crucial aspect of PEMB roof design. Roof panels come in various profiles, including:
- Standing Seam: These panels have raised seams that interlock, providing superior weather resistance. They are often used in commercial and industrial buildings.
- Corrugated: Corrugated panels have a wavy pattern that provides strength and durability. They are commonly used in agricultural and residential buildings.
- Ribbed: Ribbed panels have a series of raised ribs that add strength and rigidity. They are versatile and can be used in various building types.
The thickness of the panels, typically measured in gauges, also impacts their performance. Thicker panels offer greater durability and load-bearing capacity.
Insulation Options
Insulation is a critical component of PEMB roofs, affecting energy efficiency, comfort, and condensation control. Here are some common insulation options:
- Fiberglass Batts: These are easy to install and provide good thermal resistance. They are often used in conjunction with a vapor barrier to prevent moisture buildup.
- Spray Foam: Spray foam insulation offers excellent thermal performance and can fill gaps and voids, providing an airtight seal. It is ideal for complex roof geometries.
- Reflective Insulation: Reflective insulation consists of a reflective foil layer that reflects radiant heat. It is commonly used in hot climates to reduce cooling costs.
Ventilation Considerations
Proper ventilation is essential for maintaining a healthy indoor environment and prolonging the life of the roof. Ventilation helps to:
- Prevent Condensation: Adequate ventilation reduces the risk of condensation, which can lead to mold growth and structural damage.
- Regulate Temperature: Ventilation helps to regulate the temperature inside the building, improving comfort and reducing energy costs.
- Remove Moisture: Effective ventilation removes moisture from the building, preventing corrosion and other moisture-related issues.
Fastening Systems
The choice of fastening system is crucial for the performance and durability of the roof. Common fastening systems include:
- Exposed Fasteners: These are screws that penetrate the roof panel and secure it to the purlins. They are easy to install but can be prone to leaks if not properly sealed.
- Concealed Fasteners: These fasteners are hidden beneath the roof panels, providing a clean appearance and reducing the risk of leaks. Standing seam panels typically use concealed fasteners.
Flashing and Trim Details
Flashing and trim are used to seal joints, edges, and penetrations in the roof. Proper installation of flashing and trim is essential for preventing water infiltration and ensuring the roof’s longevity. Common flashing and trim components include:
- Ridge Cap: This covers the ridge of the roof, preventing water from entering at the highest point.
- Eave Trim: Eave trim seals the edges of the roof at the eaves, preventing water from entering the building.
- Valley Flashing: Valley flashing is used in roof valleys to channel water away from the roof and into the gutters.
Maintenance and Inspection
Regular maintenance and inspection are crucial for ensuring the longevity and performance of a PEMB roof. Key maintenance tasks include:
- Inspecting for Damage: Regularly inspect the roof for signs of damage, such as loose or missing panels, rust, and leaks.
- Cleaning Gutters and Downspouts: Keeping gutters and downspouts clear of debris prevents water buildup and potential roof damage.
- Checking Fasteners: Inspect fasteners for signs of corrosion or loosening and replace them as needed.
- Inspecting Flashing and Trim: Ensure that flashing and trim are securely in place and free of damage.
Advantages of Pre Engineered Metal Building Roofs
PEMB roofs offer several advantages over traditional roofing systems:
- Durability: Metal roofs are highly durable and can withstand harsh weather conditions, including high winds, hail, and heavy snow.
- Low Maintenance: Metal roofs require minimal maintenance compared to traditional roofing materials.
- Energy Efficiency: Metal roofs can be highly energy-efficient, especially when combined with proper insulation and reflective coatings.
- Cost-Effectiveness: PEMB roofs are often more cost-effective than traditional roofing systems due to their prefabricated nature and ease of installation.
- Sustainability: Metal roofs are environmentally friendly, as they are often made from recycled materials and are fully recyclable at the end of their lifespan.
Conclusion
Understanding Pre Engineered Metal Building Roof Details is essential for anyone involved in the design, construction, or maintenance of these structures. By choosing the right roof panels, insulation, fastening systems, and ventilation, you can ensure that your PEMB roof performs well and lasts for many years. Regular maintenance and inspection are also crucial for preserving the roof’s integrity and protecting your investment.



Leave a Reply