Flat roofs are a popular choice for many modern buildings due to their sleek appearance and practicality. However, selecting the right type of flat roof system can be crucial for ensuring durability, energy efficiency, and overall performance. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various types of flat roof systems, their benefits, and considerations to help you make an informed decision for your roofing project.
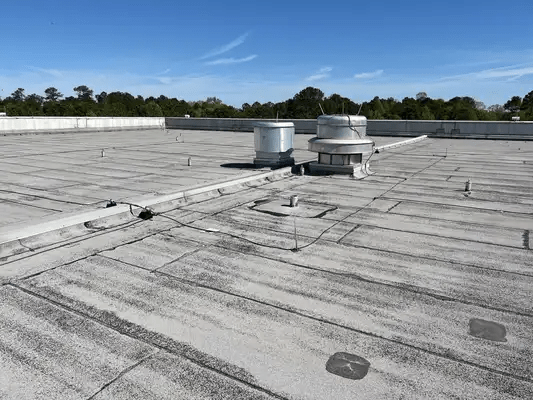

Understanding Flat Roof Systems
Flat roofs are designed with a minimal slope, typically less than 10 degrees, which helps in maximizing usable space and provides a modern aesthetic. They are commonly used in commercial buildings, residential properties, and industrial facilities. Each type of flat roof system has its own unique characteristics and advantages.
Read too: How To Replace A Mobile Home Roof: Step-by-Step Guide for Homeowners
1. Built-Up Roofing (BUR)
Built-Up Roofing (BUR) is one of the oldest and most traditional types of flat roof systems. It is made up of multiple layers of bitumen and reinforcing fabrics, which are installed in a layered system.
Components of BUR
- Bitumen Layers: Typically made from asphalt or coal tar, these layers provide waterproofing and protection.
- Reinforcing Fabrics: Layers of fabric such as fiberglass or polyester are embedded in the bitumen to add strength and durability.
- Surfacing: The top layer is usually covered with a protective coating, such as gravel or a reflective coating, to shield the underlying layers from UV radiation and physical damage.
Benefits of BUR
- Durability: BUR systems are known for their longevity, often lasting 20-30 years with proper maintenance.
- Waterproofing: The multiple layers offer excellent waterproofing and resistance to leaks.
- Fire Resistance: BUR systems are highly fire-resistant due to the inherent properties of the bitumen.
Considerations
- Weight: BUR systems can be heavy, requiring additional structural support.
- Installation: The installation process is labor-intensive and requires skilled professionals.
Types of Flat Roof Systems: Modified Bitumen Roofing
Modified Bitumen Roofing is a modern evolution of traditional BUR systems. It uses modified bitumen, which is bitumen combined with polymer modifiers to enhance its performance.
Components of Modified Bitumen Roofing
- Base Sheet: The first layer is a base sheet made from a polymer-modified bitumen.
- Saturated Membrane: This layer consists of a fabric that is saturated with modified bitumen.
- Top Layer: The final layer is typically a cap sheet, which can be smooth or granulated, providing additional protection and aesthetics.
Benefits of Modified Bitumen Roofing
- Flexibility: The polymer modification provides flexibility, which helps the roof withstand temperature fluctuations and minor structural movements.
- Ease of Installation: Modified bitumen systems can be installed using various methods, including torch-down, cold adhesive, or self-adhered, making them versatile and easy to apply.
- Low Maintenance: These systems are relatively low maintenance and offer good resistance to weathering.
Considerations
- Cost: Modified bitumen roofing can be more expensive than traditional BUR systems.
- Heat Sensitivity: During installation, the heat from the torch can be a safety concern if not handled properly.
Types of Flat Roof Systems: Single-Ply Roofing
Single-Ply Roofing systems are composed of a single layer of synthetic membrane. They are popular for their ease of installation and flexibility. The main types of single-ply roofing include:
1. Thermoplastic Olefin (TPO)
TPO is a type of single-ply roofing membrane made from a blend of polypropylene and ethylene-propylene rubber.
Benefits of TPO
- Energy Efficiency: TPO membranes are reflective, helping to reduce cooling costs by reflecting sunlight and heat.
- Durability: TPO is resistant to UV radiation, chemicals, and punctures.
- Cost-Effective: TPO systems are generally less expensive compared to other single-ply options.
Considerations
- Longevity: TPO roofing has a shorter track record compared to other single-ply systems, which can be a concern for some property owners.
- Heat Welding: Proper installation requires heat welding, which necessitates skilled labor.
2. Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM)
EPDM is a type of synthetic rubber roofing membrane known for its durability and flexibility.
Benefits of EPDM
- Long Lifespan: EPDM roofs can last 30-50 years with proper maintenance.
- Weather Resistance: EPDM is highly resistant to extreme temperatures, UV radiation, and ozone.
- Easy Installation: EPDM can be installed using adhesive, mechanical fasteners, or as a fully adhered system.
Considerations
- Aesthetic Options: EPDM is typically available in black or white, which may limit design options.
- Seam Integrity: Proper seam sealing is crucial to prevent leaks and ensure longevity.
3. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
PVC roofing systems are made from a single layer of polyvinyl chloride. They are known for their strength and resistance to environmental factors.
Benefits of PVC
- Durability: PVC roofs are resistant to chemicals, grease, and fire, making them suitable for a variety of applications.
- Reflectivity: Like TPO, PVC membranes are reflective and help reduce cooling costs.
- Seam Strength: PVC seams are heat-welded, providing strong, watertight seals.
Considerations
- Cost: PVC roofing can be more expensive compared to TPO and EPDM.
- Environmental Concerns: The production of PVC can have environmental impacts, though advances in manufacturing processes are addressing these concerns.
Types of Flat Roof Systems: Green Roofs
Green roofs, also known as living roofs, incorporate vegetation into the roofing system. They provide a unique aesthetic and environmental benefits.
1. Intensive Green Roofs
Intensive green roofs are designed to support a wide variety of plants, including shrubs and small trees.
Benefits of Intensive Green Roofs
- Insulation: They provide excellent thermal insulation, reducing heating and cooling costs.
- Stormwater Management: Green roofs can absorb and slow down rainwater runoff, reducing strain on drainage systems.
- Biodiversity: They create habitats for birds, insects, and other wildlife.
Considerations
- Weight: Intensive green roofs are heavy and require strong structural support.
- Maintenance: They require regular maintenance to ensure plant health and system performance.
2. Extensive Green Roofs
Extensive green roofs are lighter and designed for low-growing vegetation, such as grasses and mosses.
Benefits of Extensive Green Roofs
- Lower Weight: Extensive green roofs are lighter and require less structural support compared to intensive systems.
- Low Maintenance: They are relatively low maintenance and suitable for a wide range of building types.
- Cost-Effective: Generally, extensive green roofs are less expensive to install and maintain.
Considerations
- Limited Plant Options: The range of plants is limited to low-growing species.
- Installation: Proper installation is critical to ensure the roof’s ability to support plant growth and manage water.
Conclusion
Choosing the right types of flat roof systems involves understanding the specific needs of your building, your budget, and your long-term goals. Whether you opt for traditional BUR systems, modern single-ply membranes, or innovative green roofs, each option has its own set of benefits and considerations. By evaluating these factors and consulting with roofing professionals, you can select the flat roof system that best meets your requirements and ensures lasting performance and protection for your property.


Leave a Reply