Flat roofs are a popular choice for commercial buildings due to their sleek appearance and practical benefits. Understanding the various types of flat roofs available can help you make informed decisions about which roofing system best suits your building’s needs. This guide will explore the different types of flat roofs commercial properties commonly use, their benefits, and considerations for each type.
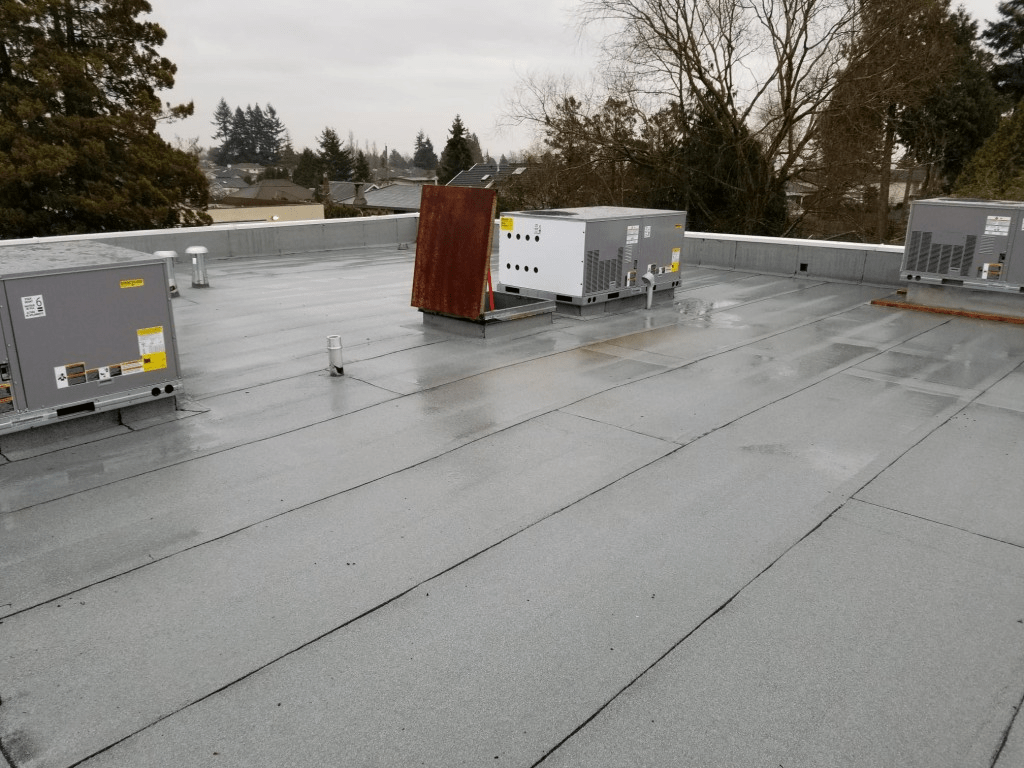
Why Choose a Flat Roof for Commercial Buildings?
Flat roofs are often chosen for commercial buildings because of their:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Flat roofs generally cost less to install and maintain compared to pitched roofs.
- Space Utilization: They provide additional usable space for HVAC systems, solar panels, and roof gardens.
- Modern Aesthetics: Flat roofs contribute to a contemporary and clean architectural look.
Read too: How To Replace A Mobile Home Roof: Step-by-Step Guide for Homeowners
Types of Flat Roofs Commercial Buildings Use
1. Built-Up Roofing (BUR)
Overview
Built-Up Roofing (BUR) is one of the oldest and most traditional types of flat roofing systems. It consists of multiple layers of bitumen (asphalt) and reinforcing fabrics. This method is often referred to as a “tar and gravel” roof due to its layered composition.
Components
- Base Sheet: The first layer that adheres to the roof deck.
- Bitumen Layers: Multiple layers of asphalt or coal tar are applied over the base sheet.
- Top Layer: Typically consists of a layer of gravel or a reflective coating to protect against UV rays and weathering.
Benefits
- Durability: BUR systems are known for their long lifespan and ability to withstand harsh weather conditions.
- Fire Resistance: The bitumen layers offer good fire resistance.
- Low Maintenance: BUR roofs are relatively low-maintenance and can last 20-30 years with proper care.
Considerations
- Installation: The installation process can be labor-intensive and time-consuming.
- Weight: BUR roofs are heavier than some other flat roofing options, which may require additional structural support.
2. Modified Bitumen Roofing
Overview
Modified Bitumen Roofing is an evolution of traditional BUR systems, incorporating modifications to the bitumen to enhance performance. The most common modifications are the addition of polymers, which improve elasticity and UV resistance.
Components
- Base Layer: Similar to BUR but with modified bitumen.
- Modified Bitumen Sheets: Rolls of bitumen modified with polymers are applied over the base layer.
- Top Coating: Can be granulated for added protection or smooth.
Benefits
- Flexibility: The modified bitumen is more flexible than traditional BUR, making it more resistant to cracking and movement.
- Ease of Installation: Can be installed using heat, cold adhesives, or self-adhesive methods.
- Weather Resistance: Offers excellent protection against UV rays and temperature fluctuations.
Considerations
- Cost: Modified bitumen roofing is generally more expensive than BUR.
- Maintenance: Although durable, it may require periodic inspections to ensure the integrity of the seams and joints.
3. Thermoplastic Olefin (TPO) Roofing
Overview
Thermoplastic Olefin (TPO) roofing is a single-ply membrane roofing system that has gained popularity for its energy efficiency and ease of installation. It is made from a blend of polypropylene and ethylene-propylene rubber.
Components
- TPO Membrane: A single-ply layer that is applied to the roof deck.
- Adhesive or Mechanical Fasteners: Used to secure the membrane to the roof structure.
- Seam Tapes: Applied to seams to ensure a watertight seal.
Benefits
- Energy Efficiency: TPO membranes are reflective, which helps reduce cooling costs by reflecting sunlight and heat.
- Durability: Offers good resistance to punctures, tears, and chemical exposure.
- Installation: Lightweight and easy to install, with options for adhesive, mechanical fasteners, or a combination of both.
Considerations
- Color Options: Limited color choices compared to other roofing systems.
- Performance Variability: Quality can vary between manufacturers, so it’s essential to choose a reputable supplier.
4. Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) Roofing
Overview
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) is a type of synthetic rubber roofing that is widely used in flat roofing systems. It is known for its durability and weather resistance.
Components
- EPDM Membrane: A single-ply membrane made from synthetic rubber.
- Adhesive or Mechanical Fasteners: Used to attach the membrane to the roof deck.
- Sealants: Applied to seams and joints to prevent leaks.
Benefits
- Durability: EPDM is highly resistant to weathering, UV rays, and extreme temperatures.
- Flexibility: Remains flexible in varying temperatures, reducing the risk of cracking.
- Low Maintenance: Minimal upkeep is required once installed.
Considerations
- Appearance: EPDM is typically black, which can absorb heat; white or reflective options are available but may be less common.
- Seam Integrity: Proper sealing of seams is crucial to prevent leaks.
5. PVC Roofing
Overview
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) roofing is a single-ply membrane roofing system known for its strength and resistance to chemicals. It is widely used in commercial applications due to its performance characteristics.
Components
- PVC Membrane: A single layer of PVC that is applied to the roof deck.
- Adhesives or Heat Welding: Used to secure the membrane and seal seams.
- Protective Coating: Often includes a coating to enhance UV resistance.
Benefits
- Chemical Resistance: PVC roofs are highly resistant to chemicals and pollutants.
- Longevity: Provides a long-lasting roofing solution with a lifespan of 20-30 years.
- Reflective: Helps reduce cooling costs by reflecting UV rays.
Considerations
- Cost: PVC roofing can be more expensive than other flat roofing options.
- Installation: Requires skilled installers to ensure proper heat welding and seam integrity.
Conclusion
Choosing the right types of flat roofs commercial buildings can be a crucial decision that impacts the building’s performance, longevity, and appearance. Each roofing system—whether Built-Up Roofing, Modified Bitumen, TPO, EPDM, or PVC—has its unique benefits and considerations. Understanding these options can help you select the best roofing solution for your commercial property based on factors like durability, cost, energy efficiency, and ease of maintenance.

Leave a Reply