When it comes to maintaining the integrity of your roof, one critical component often overlooked is roof flashing. Understanding what roof flashing is made of can help homeowners make informed decisions about their roofing needs and ensure their home remains protected from water damage. This article provides a thorough overview of roof flashing materials, their purposes, and their benefits.
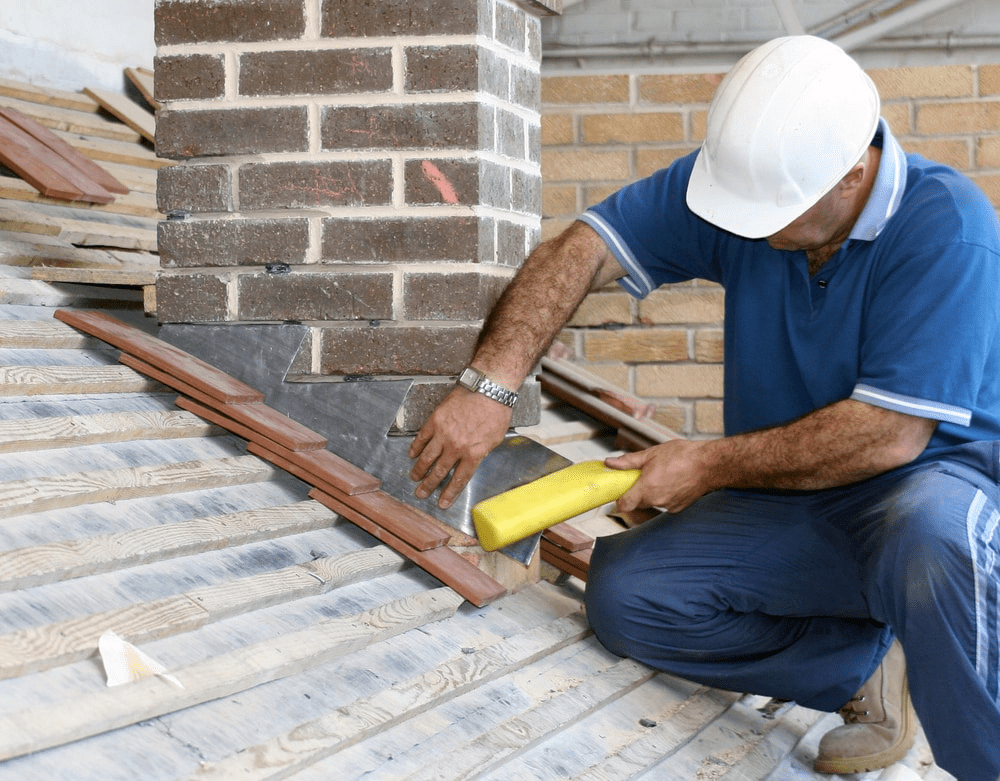

What Is Roof Flashing?
Roof flashing is a material used to direct water away from critical areas of a roof and prevent leaks. It’s typically installed around joints, seams, and other vulnerable spots where the roof meets other structures, such as chimneys, vents, skylights, and dormers. The primary function of roof flashing is to ensure that water flows away from these areas, reducing the risk of leaks and water damage.
Read too: Is It Reasonable to Ask the Seller to Replace the Roof?
What Is Roof Flashing Made Of?
Roof flashing can be made from a variety of materials, each with its own set of advantages and applications. Here’s a detailed look at the common materials used in roof flashing:
1. Aluminum
- Characteristics: Aluminum is a popular choice for roof flashing due to its lightweight, corrosion-resistant properties. It is easy to work with and can be shaped to fit various roof configurations.
- Advantages: Aluminum flashing is highly durable and offers excellent resistance to rust and weathering. It’s also cost-effective and can be painted to match the roof color.
- Applications: Ideal for use in a wide range of climates and roofing types, including residential and commercial buildings.
2. Copper
- Characteristics: Copper is a premium material known for its longevity and aesthetic appeal. It develops a distinctive green patina over time, which many homeowners find attractive.
- Advantages: Copper is highly resistant to corrosion and has a long lifespan. It also offers superior durability and strength, making it ideal for high-end roofing applications.
- Applications: Often used in historical restoration projects, high-end residential roofing, and areas where aesthetics are a significant concern.
3. Lead
- Characteristics: Lead flashing is a traditional material that has been used for centuries. It is highly malleable, allowing it to be easily shaped and installed around complex roof features.
- Advantages: Lead is extremely durable and resistant to weathering. Its flexibility makes it suitable for intricate roof designs and challenging installation scenarios.
- Applications: Commonly used in historic buildings and restoration projects where traditional methods are preferred. However, due to environmental and health concerns, its use is decreasing.
4. Steel
- Characteristics: Steel flashing is typically galvanized or coated to prevent rust and enhance durability. It is a strong and sturdy material often used in commercial roofing.
- Advantages: Steel flashing offers excellent strength and resistance to impact. It is also relatively inexpensive compared to other metals.
- Applications: Suitable for commercial buildings and areas where additional strength is required, such as around roof penetrations and high-traffic areas.
5. Rubber and Synthetic Materials
- Characteristics: Rubber and synthetic flashing materials, such as EPDM (ethylene propylene diene monomer) and TPO (thermoplastic olefin), are modern alternatives to traditional metals.
- Advantages: These materials are flexible, lightweight, and resistant to UV rays and extreme temperatures. They also offer excellent water resistance and are easy to install.
- Applications: Commonly used in flat or low-slope roofs, particularly in commercial applications and areas where traditional flashing materials might not be suitable.
6. Plastic
- Characteristics: Plastic flashing materials, including PVC (polyvinyl chloride) and ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene), are used in various roofing applications.
- Advantages: Plastic flashing is lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and easy to install. It is also cost-effective and available in various colors and styles.
- Applications: Ideal for residential roofing projects and areas where moisture resistance is essential, such as around vents and skylights.
Why Is Roof Flashing Important?
Understanding what roof flashing is made of and its significance can help you appreciate its role in roof maintenance and repair. Here’s why roof flashing is crucial:
1. Prevents Water Damage
Roof flashing directs water away from vulnerable areas, preventing it from seeping into the roof structure. This reduces the risk of water damage, mold growth, and structural deterioration.
2. Enhances Roof Longevity
Properly installed and maintained flashing extends the life of your roof by protecting critical joints and seams from water infiltration. This helps avoid premature roof replacement and costly repairs.
3. Improves Energy Efficiency
By preventing leaks and water damage, roof flashing helps maintain a well-insulated and weather-tight roof. This can improve your home’s energy efficiency by reducing heat loss and preventing drafts.
4. Protects Against Weather Conditions
Flashing materials are designed to withstand various weather conditions, including heavy rain, snow, and wind. This ensures that your roof remains protected and functional throughout the year.
How to Maintain Roof Flashing
Proper maintenance is key to ensuring the effectiveness of roof flashing. Here are some tips to keep your roofs flashing in top condition:
1. Regular Inspections
Inspect your roof flashing regularly, especially after severe weather events. Look for signs of damage, such as rust, cracks, or loose flashing.
2. Clean and Remove Debris
Keep the area around your roof flashing clean and free of debris, such as leaves and branches. This helps prevent water from pooling and reduces the risk of damage.
3. Check for Leaks
Monitor your home for signs of leaks or water damage, such as stains on the ceiling or walls. If you notice any issues, address them promptly to prevent further damage.
4. Professional Maintenance
Consider hiring a professional roofing contractor to inspect and maintain your roofs flashing. They can identify potential issues and perform necessary repairs or replacements.
Conclusion
Knowing what roofs flashing is made of is essential for understanding its role in protecting your home. Whether it’s aluminum, copper, lead, steel, rubber, synthetic materials, or plastic, each type of flashing material offers unique benefits and applications. By selecting the right material and ensuring proper installation and maintenance, you can safeguard your roof against leaks and water damage, ultimately extending its lifespan and enhancing your home’s overall durability.

Leave a Reply