Many homeowners notice small openings or ventilators placed near the roof and wonder, Why Are Ventilators Provided Near The Roof Of A House in the first place? This question usually comes up when indoor rooms feel hot, humid, or poorly ventilated despite open windows. Understanding the purpose of roof-level ventilators can help you improve comfort, protect your home’s structure, and even reduce energy costs.
Why Are Ventilators Provided Near The Roof Of A House?
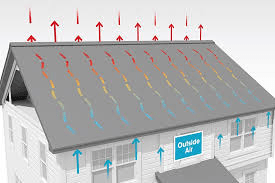
Ventilators are provided near the roof of a house primarily to remove hot air, moisture, and stale air that naturally rise upward. Warm air is lighter than cool air, so it accumulates near the ceiling and roof. By placing ventilators at this highest point, homes can efficiently release trapped heat and maintain healthier airflow.
Read too: How To Replace Roof Shingles That Blew Off: A Comprehensive Guide
This design principle is based on natural convection, a basic physical process that has been used in building design for centuries. Modern homes still rely on this simple but effective concept to improve indoor air quality and thermal comfort.
How Does Hot Air Movement Affect Home Ventilation?
The Science Behind Rising Hot Air
Hot air rises because it is less dense than cool air. Inside a house, heat from people, appliances, cooking, and sunlight moves upward and gathers near the roof or attic.
Without proper ventilation:
- Heat becomes trapped
- Indoor temperatures rise
- Humidity increases
- Living spaces feel stuffy
Roof-level ventilators allow this hot air to escape naturally, making room for cooler air to enter from lower openings such as windows or wall vents.
Stack Effect Explained Simply
This airflow pattern is known as the stack effect:
- Cool air enters from lower openings
- Warm air rises through the house
- Hot air exits through roof ventilators
This continuous cycle improves comfort without relying entirely on mechanical systems.
Why Not Place Ventilators Lower in the House?
Many people ask why ventilators aren’t installed only at lower wall levels. The reason is efficiency.
Lower-level ventilators alone cannot remove trapped heat effectively because:
- Hot air stays near the ceiling
- Moist air collects in the upper areas
- Air circulation becomes incomplete
By placing ventilators near the roof, homes use gravity and physics to their advantage, allowing heat and moisture to escape naturally.
Key Benefits of Roof-Level Ventilators
1. Improved Indoor Temperature Control
Roof ventilators help release excess heat, especially in hot climates. Studies show that proper attic ventilation can reduce indoor temperatures by 10–15°F (5–8°C) during summer months, lowering dependence on air conditioning.
2. Better Indoor Air Quality
Ventilation near the roof removes:
- Stale air
- Odors from cooking
- Pollutants and airborne particles
This is especially important in kitchens, bathrooms, and attic spaces.
3. Moisture and Mold Prevention
Warm, moist air trapped near the roof can condense and cause:
- Mold growth
- Wood rot
- Insulation damage
Roof ventilators reduce humidity buildup, protecting structural components over time.
4. Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
By reducing heat buildup, ventilators help air conditioners work less. According to building efficiency studies, proper ventilation can lower cooling costs by up to 15% annually in warm regions.
Common Types of Roof Ventilators
| Type of Ventilator | How It Works | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Ridge Vent | Runs along roof peak, passive airflow | Modern homes |
| Turbine Vent | Spins using wind power | Hot, windy areas |
| Gable Vent | Mounted on wall near roof | Traditional houses |
| Solar Vent | Powered by sunlight | Energy-efficient homes |
Each type serves the same core purpose: releasing hot air from the highest point of the house.
Why Are Ventilators Provided Near The Roof Of A House in Hot Climates?
In hot and tropical regions, roof ventilators are even more critical. Sunlight directly heats the roof surface, transferring heat into attic spaces.
Without ventilation:
- Attic temperatures can exceed 150°F (65°C)
- Heat radiates downward into living areas
Roof ventilators prevent this heat buildup and make homes more livable, especially in regions with long summers.
Role of Roof Ventilators in Modern Home Design
Passive Cooling Strategies
Architects increasingly use roof ventilation as part of passive cooling, reducing reliance on mechanical cooling systems. This approach:
- Saves energy
- Reduces carbon footprint
- Improves long-term sustainability
Compliance With Building Standards
Many building codes recommend or require roof ventilation to:
- Protect roofing materials
- Improve occupant health
- Extend building lifespan
For more technical background on ventilation principles, you can refer to ventilation concepts explained on Wikipedia.org, which provides an authoritative overview of airflow and building ventilation systems.
Advantages vs. Disadvantages of Roof Ventilators
Advantages
- Natural airflow without electricity
- Lower indoor temperatures
- Reduced moisture damage
- Improved air quality
Disadvantages
- Poor installation can cause leaks
- Requires proper intake vents to work effectively
- Initial installation cost
When designed correctly, the advantages significantly outweigh the drawbacks.
Step-by-Step: How Roof Ventilators Improve Airflow
- Fresh air enters through lower openings (windows or wall vents)
- Indoor heat sources warm the air
- Warm air rises toward the ceiling
- Roof ventilators release trapped hot air
- Continuous airflow cycle improves comfort
This simple process works 24/7 without manual operation.
FAQ: Roof Ventilators Explained
Do all houses need roof ventilators?
Yes, most houses benefit from roof ventilators, especially those in warm or humid climates where heat and moisture buildup are common.
Can roof ventilators reduce electricity bills?
Absolutely. By lowering indoor temperatures naturally, roof ventilators reduce air conditioning usage and energy costs.
Are roof ventilators effective in cold climates?
Yes. In cold regions, they help prevent moisture accumulation and condensation that can damage insulation and roofing materials.
How many roof ventilators does a house need?
It depends on roof size and attic area. A general guideline is 1 square foot of ventilation for every 300 square feet of attic space.
Can roof ventilators cause water leaks?
Only if installed incorrectly. Professional installation and proper flashing prevent leaks.
Conclusion
So, why are ventilators provided near the roof of a house? The answer lies in simple physics, comfort, and long-term home protection. Roof-level ventilators allow hot air and moisture to escape naturally, improving indoor air quality, reducing energy costs, and extending the life of your home.
If you found this guide helpful, share it on social media to help other homeowners understand the importance of proper roof ventilation and make smarter home design decisions.


Leave a Reply