Introduction
A new roof is one of the most significant home improvements a homeowner can make. It provides better protection, improves curb appeal, and can even enhance energy efficiency. However, some homeowners notice temperature fluctuations after installing a new roof, raising concerns about whether their home is losing heat.
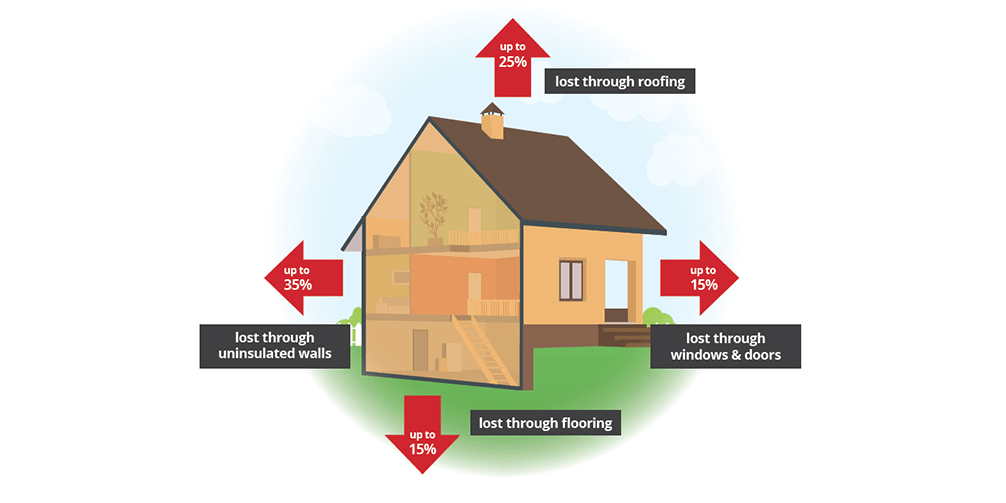
Can a house lose heat from a new roof installed? The short answer is yes, but it depends on several factors, including ventilation, insulation, and roofing materials. In this article, we’ll explore how a new roof can impact heat retention, potential causes of heat loss, and how to ensure your home remains energy-efficient.
Read too: Is It Reasonable to Ask the Seller to Replace the Roof?
Can A House Lose Heat From A New Roof Installed?
Yes, a house can lose heat after a new roof installation, but this is not always due to the roof itself. Several factors can contribute to heat loss, including improper installation, poor insulation, and inadequate ventilation. Let’s break down the main reasons why this might happen.
1. Poor or Insufficient Insulation
One of the most common reasons a house may lose heat after a new roof is installed is inadequate insulation. If the insulation was removed, damaged, or not properly replaced during the roofing process, it could allow warm air to escape through the attic.
How insulation affects heat retention:
- Proper insulation acts as a barrier, preventing heat from escaping in winter and keeping the house cool in summer.
- Missing or damaged insulation creates gaps that allow warm air to escape, making the home less energy-efficient.
- Different insulation types (fiberglass, spray foam, cellulose) have varying effectiveness levels, and the right type should be used for maximum efficiency.
2. Changes in Roof Ventilation
Ventilation plays a crucial role in maintaining a home’s temperature balance. A well-ventilated attic helps regulate temperature and prevents moisture buildup. However, if the roof’s ventilation was altered during installation, it might lead to unexpected heat loss.
Common ventilation issues after a roof replacement:
- Too many vents installed – Excessive ventilation can lead to warm air escaping too quickly.
- Blocked or sealed vents – If existing vents were accidentally blocked or removed, trapped warm air can cause condensation and other issues.
- Improper vent placement – Poor vent placement can disrupt airflow, leading to inefficient heat retention.
3. Roofing Materials and Heat Reflection
The materials used in the new roof can also influence heat retention. Some materials naturally reflect more heat than others, which can impact indoor temperatures.
How roofing materials affect heat retention:
- Asphalt shingles – Moderate heat absorption; traditional black shingles retain more heat, while lighter colors reflect it.
- Metal roofing – Highly reflective, which can reduce heat absorption and make the house cooler in winter.
- Clay and tile roofs – Natural insulators that help maintain indoor temperatures.
- Cool roofing technology – Some modern materials are designed to reflect more sunlight, which may reduce heat retention.
If a homeowner switches from a heat-absorbing roof (like dark asphalt) to a highly reflective material (like metal), they might notice their home feels cooler in winter.
4. Air Leaks and Poor Sealing
If the roof installation was not done correctly, air leaks might be present, allowing heat to escape through small gaps. These leaks can occur around chimneys, skylights, vents, and roof edges.
How to identify air leaks:
- Feeling drafts near the attic or upper levels.
- Noticing higher energy bills after the roof replacement.
- Conducting a professional energy audit to detect heat loss areas.
Proper sealing and flashing around roof openings can help prevent air leaks and improve energy efficiency.
How to Prevent Heat Loss from a New Roof
If you’re concerned about losing heat after a new roof installation, there are several steps you can take to minimize the issue.
1. Ensure Proper Insulation
Adding or upgrading attic insulation is one of the most effective ways to prevent heat loss. If insulation was removed during the roofing process, make sure it’s properly replaced with the right R-value for your climate.
Recommended insulation R-values by climate zone:
- Cold climates (Zone 6-8): R49-R60
- Moderate climates (Zone 4-5): R38-R49
- Warm climates (Zone 1-3): R30-R38
2. Optimize Roof Ventilation
Proper ventilation helps regulate indoor temperature and prevents issues like condensation and mold. If you suspect ventilation is causing heat loss, consult a professional roofer to ensure vents are correctly positioned and balanced.
Best practices for ventilation:
- Maintain a balance between intake (soffit vents) and exhaust (ridge vents) ventilation.
- Avoid over-ventilating, which can cause excessive heat loss.
- Check for obstructions in vent openings.
3. Choose the Right Roofing Material
If you’re in a cold climate, selecting a roof with better heat retention properties can help maintain warmth in winter. Some options include:
- Dark-colored shingles (absorb more heat).
- Clay tiles (natural insulators).
- Properly installed asphalt shingles with good underlayment.
If you live in a warmer climate, a reflective or cool roof may be more beneficial to reduce cooling costs in summer.
4. Seal Air Leaks
Sealing air leaks around the roofline, attic, and ventilation areas can prevent warm air from escaping. Some effective solutions include:
- Using weatherstripping around attic doors.
- Applying spray foam or caulk to seal gaps.
- Ensuring flashing around chimneys and vents is properly installed.
5. Conduct a Home Energy Audit
If you’re unsure whether your house is losing heat from the new roof, consider getting a professional energy audit. This process involves testing for air leaks, insulation gaps, and overall home efficiency. Many utility companies offer free or low-cost energy audits.
Conclusion
So, can a house lose heat from a new roof installed? Yes, but it’s often due to factors such as insufficient insulation, poor ventilation, reflective roofing materials, or air leaks rather than the roof itself.
If you notice significant heat loss after a roof replacement, it’s essential to evaluate insulation, ventilation, and sealing to ensure your home remains energy-efficient. By taking the right steps, you can prevent unnecessary heat loss, lower your energy bills, and maintain a comfortable indoor temperature all year round.



Leave a Reply