When it comes to constructing a pre-engineered metal building (PEMB), one of the most critical aspects to consider is the roof. The roof is not only responsible for protecting the building from environmental factors but also plays a significant role in the overall structural integrity and energy efficiency of the building. In this article, we will delve deep into the essential pre-engineered metal building roof details that you need to know. We’ll cover the types of roofs available, the materials used, insulation options, and maintenance tips to ensure longevity and durability.
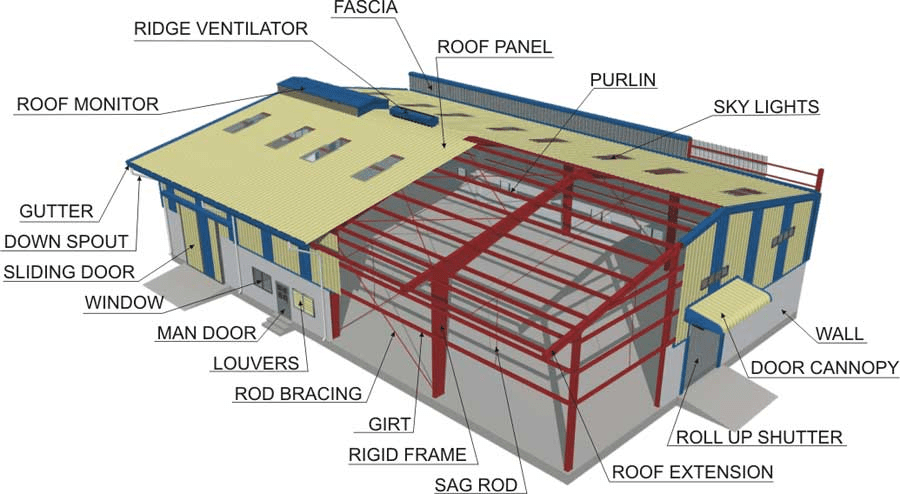
What Are Pre-Engineered Metal Buildings?
Before we get into the specific roof details, it’s important to understand what pre-engineered metal buildings are. PEMBs are structures designed and manufactured in a factory and then assembled on-site. They are popular in a variety of industries due to their cost-effectiveness, durability, and versatility. These buildings are commonly used for commercial, industrial, agricultural, and even residential purposes.
Read too: How To Replace A Mobile Home Roof: Step-by-Step Guide for Homeowners
Importance of Pre-Engineered Metal Building Roof Details
The roof is one of the most vital components of any building, and in a PEMB, it’s no different. The roof’s design, material, and installation can significantly impact the building’s performance, including its resistance to weather, insulation, and longevity. Properly designed and installed roofs can also contribute to energy savings and lower maintenance costs over time.
Types of Roofs for Pre-Engineered Metal Buildings
1. Gable Roof
The gable roof is one of the most common roof types for pre-engineered metal buildings. It features two sloping sides that meet at a ridge in the middle. This type of roof is popular due to its simplicity, ease of installation, and efficient water drainage. The gable design also provides ample space for insulation, which can help in maintaining the building’s temperature.
2. Single Slope Roof
The single slope roof has one slope that extends from one side of the building to the other. This design is often used for smaller buildings or extensions to existing structures. It offers efficient water drainage and can be ideal for buildings in areas with heavy rainfall. The single slope roof is also easier to install and can be more cost-effective than other designs.
3. Hip Roof
A hip roof has slopes on all four sides, which meet at a point or ridge. This type of roof is highly durable and provides excellent wind resistance, making it suitable for buildings in areas prone to strong winds or hurricanes. The hip roof design also offers better ventilation and can be aesthetically pleasing.
4. Gambrel Roof
The gambrel roof is a two-sided roof with two slopes on each side. The upper slope is typically shallow, while the lower slope is steeper. This design is often used in agricultural buildings, such as barns, as it provides extra storage space in the upper area of the building. Gambrel roofs are also known for their unique appearance.
5. Flat Roof
Although not as common as the other designs, flat roofs are sometimes used in pre-engineered metal buildings, especially in commercial applications. Flat roofs are easier to construct and maintain, and they provide additional usable space for HVAC units or solar panels. However, they may require more maintenance to prevent water pooling and leaks.
Materials Used in Pre-Engineered Metal Building Roofs
The choice of material for the roof is crucial in determining the building’s durability, energy efficiency, and overall cost. Here are some of the most common materials used in PEMB roofs:
1. Steel
Steel is the most common material used for pre-engineered metal building roofs. It is highly durable, resistant to weather and fire, and can last for decades with proper maintenance. Steel roofs can be coated with various materials, such as galvanized or galvalume coatings, to enhance their corrosion resistance.
2. Aluminum
Aluminum is another popular material for PEMB roofs. It is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and energy-efficient. Aluminum roofs reflect sunlight, which can help reduce cooling costs in hot climates. However, aluminum is generally more expensive than steel, which can increase the overall cost of the building.
3. Copper
Copper roofs are known for their durability and aesthetic appeal. Over time, copper develops a green patina that adds character to the building. Copper is also highly resistant to corrosion and can last for more than 50 years. However, it is one of the most expensive roofing materials, which may not be suitable for all budgets.
4. Zinc
Zinc is a premium roofing material that offers excellent durability and corrosion resistance. It is often used in high-end applications due to its long lifespan and low maintenance requirements. Zinc roofs can also develop a patina over time, similar to copper, which can enhance the building’s appearance.
Insulation Options for Pre-Engineered Metal Building Roofs
Proper insulation is essential for maintaining the energy efficiency of a pre-engineered metal building. Insulation helps regulate the building’s temperature, reduces energy costs, and prevents condensation, which can lead to mold and mildew. Here are some common insulation options:
1. Fiberglass Insulation
Fiberglass insulation is one of the most commonly used insulation materials in pre-engineered metal buildings. It is cost-effective, easy to install, and provides good thermal performance. Fiberglass insulation can be installed in batts or rolls and is often placed between the roof panels and the interior ceiling.
2. Rigid Board Insulation
Rigid board insulation is made from materials such as polyisocyanurate, polystyrene, or polyurethane. It offers higher insulation values compared to fiberglass and is more resistant to moisture. Rigid board insulation is often used in buildings where energy efficiency is a top priority.
3. Spray Foam Insulation
Spray foam insulation is applied directly to the underside of the roof panels. It expands to fill gaps and cracks, providing an airtight seal. Spray foam insulation offers excellent thermal performance and can help prevent condensation. However, it is more expensive than other insulation options and requires professional installation.
4. Reflective Insulation
Reflective insulation is typically installed under the roof panels and works by reflecting radiant heat away from the building. It is often used in conjunction with other insulation materials to enhance energy efficiency. Reflective insulation is particularly effective in hot climates where reducing heat gain is essential.
Maintenance Tips for Pre-Engineered Metal Building Roofs
To ensure the longevity and performance of your pre-engineered metal building roof, regular maintenance is essential. Here are some tips to keep your roof in top condition:
1. Regular Inspections
Schedule regular inspections of your roof, especially after severe weather events. Look for signs of damage, such as dents, scratches, or loose fasteners. Address any issues promptly to prevent further damage.
2. Cleaning
Keep your roof clean by removing debris, such as leaves, branches, and dirt. Debris can trap moisture and cause corrosion or mold growth. Use a soft brush or a low-pressure washer to clean the roof, and avoid using harsh chemicals that can damage the roof’s coating.
3. Check for Leaks
Inspect the interior of your building for any signs of leaks, such as water stains, mold, or mildew. Leaks can indicate a problem with the roof’s seal or flashing. Address leaks immediately to prevent damage to the building’s structure and insulation.
4. Recoat the Roof
If your roof has a protective coating, it may need to be recoated periodically to maintain its effectiveness. Recoating can help prevent corrosion and extend the life of the roof. Consult the manufacturer’s guidelines for recoating intervals and recommended products.
5. Monitor Fasteners
Over time, the fasteners that secure the roof panels may become loose due to temperature fluctuations or wind. Regularly check the fasteners and tighten them as needed. If any fasteners are missing or damaged, replace them promptly.
Conclusion
Understanding the key pre-engineered metal building roof details is essential for ensuring the longevity, durability, and energy efficiency of your structure. From choosing the right roof design and material to selecting the best insulation and following proper maintenance practices, every decision plays a crucial role in the performance of your building’s roof.
By taking the time to carefully plan and maintain your pre-engineered metal building roof, you can protect your investment and ensure that your building remains in excellent condition for years to come. Whether you’re constructing a new building or maintaining an existing one, these insights will help you make informed decisions and achieve the best results.


Leave a Reply