The pitch or slope of a roof is an essential architectural element that not only contributes to the overall appearance of a building but also plays a crucial role in its functionality. The roof pitch refers to the angle at which the roof slopes, and it determines how water, snow, and debris are directed off the roof. Different types of roof pitches are used in various architectural styles and climates to optimize performance and aesthetics. In this article, we will explore the different types of roof pitches and the advantages they offer.
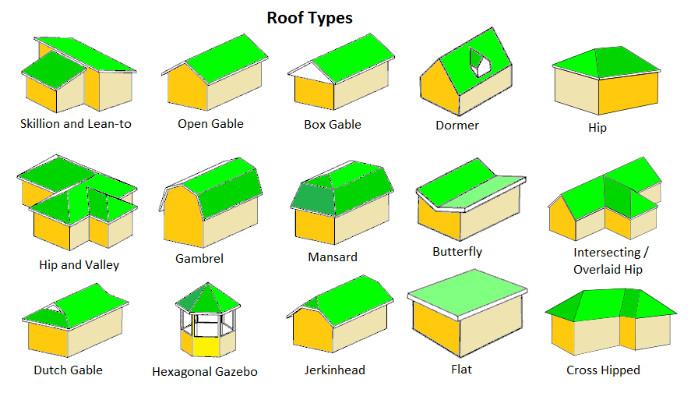
Flat Roof
Pitch: 0° to 10°
Flat roofs have little to no pitch and are common in modern architecture. While they may appear entirely flat, flat roofs typically have a slight slope to ensure proper drainage. Flat roofs are cost-effective, easy to construct, and offer additional space for rooftop gardens or solar panels. However, their minimal slope can lead to water pooling, which requires careful design and waterproofing to prevent leaks.
Low-Pitched Roof
Pitch: 10° to 20°
Low-pitched roofs strike a balance between flat roofs and steeper pitches. They are popular for homes and commercial buildings, providing sufficient slope for water runoff while maintaining a modern and contemporary look. Low-pitched roofs are relatively easy to maintain and provide more interior space compared to steeper roofs.
Medium-Pitched Roof
Pitch: 20° to 35°
Medium-pitched roofs are a popular choice for various architectural styles, including traditional and modern homes. They offer a good balance between water shedding and snow shedding capabilities. Medium-pitched roofs are versatile and can accommodate various roofing materials, making them a popular choice among homeowners.
High-Pitched Roof
Pitch: 35° and above
High-pitched roofs are common in regions with heavy snowfall, as their steep slope allows snow to easily slide off the roof. They are a hallmark of traditional and historical architecture, often seen in cottages, cabins, and Gothic-style buildings. High-pitched roofs offer excellent ventilation and allow for additional living space in the attic or upper floors.
Advantages of Different Roof Pitches
- Water and Snow Shedding: The primary purpose of roof pitches is to ensure efficient water and snow shedding. Steeper pitches allow water and snow to run off the roof more quickly, reducing the risk of water damage and snow buildup.
- Architectural Aesthetics: Different roof pitches contribute to the architectural style of a building. For example, steep pitches are common in classic and historical designs, while modern architecture often features low-pitched or flat roofs.
- Interior Space and Attic Ventilation: High-pitched roofs provide more interior space and allow for better attic ventilation, improving energy efficiency and indoor comfort.
- Roofing Material Compatibility: Certain roofing materials are better suited for specific roof pitches. For example, medium-pitched roofs suit shingles well, while high-pitched roofs commonly employ metal roofing for its durability and snow-shedding capabilities.
- Climate Considerations: Climate often influences the choice of roof pitch. Areas with heavy snowfall prefer steeper pitches, while areas with mild weather conditions may find low-pitched roofs more suitable.
Conclusion
The type of roof pitch chosen for a building significantly impacts its appearance, functionality, and performance. Each type of roof pitch offers unique advantages and considerations, making it essential to select the most appropriate pitch based on architectural style, climate, and building requirements. Whether it’s the sleek look of a flat roof, the balance of a medium-pitched roof, or the classic appeal of a high-pitched roof, understanding the different types of roof pitches helps homeowners and architects make informed decisions for a successful and aesthetically pleasing roofing solution.

Leave a Reply