If you live in an area exposed to hurricanes, heavy rain, or extreme heat, you may have wondered what is the purpose of vent on storm house roof. Roof vents are often overlooked, yet they play a critical role in protecting your home from moisture damage, heat buildup, and structural failure during storms. Understanding how roof vents work helps homeowners make smarter decisions about durability, safety, and long-term costs.
What Is the Purpose of Vent on Storm House Roof?
The primary purpose of a vent on a storm house roof is to regulate airflow through the attic and roof structure. Proper ventilation allows hot, moist air to escape while drawing in cooler, drier air from outside.
Read too: Is It Reasonable to Ask the Seller to Replace the Roof?
In Simple Terms, Roof Vents Help:
- Prevent moisture buildup
- Reduce heat trapped in the attic
- Protect the roof structure during storms
- Improve energy efficiency
- Extend the lifespan of roofing materials
In storm-prone regions, these functions are not optional—they are essential.
How Roof Vents Work During Storm Conditions
Roof vents rely on natural airflow principles. Warm air rises and exits through high vents (like ridge or box vents), while cooler air enters through low vents (such as soffit vents).
Airflow Process (Step-by-Step)
- Outdoor air enters through soffit or intake vents
- Air moves upward through the attic
- Heat and moisture escape through roof vents
- Pressure inside the roof system stabilizes
This continuous airflow reduces internal stress on the roof during high winds and pressure changes caused by storms.
Why Storm Houses Need Specialized Roof Ventilation
Storm houses are designed to withstand extreme weather. Without proper ventilation, even reinforced roofs can fail prematurely.
Key Storm-Related Problems Roof Vents Prevent
- Condensation after heavy rain
- Mold growth in humid climates
- Wood rot in roof decking
- Shingle warping from heat pressure
- Structural uplift during high winds
Building science studies show that poorly ventilated attics can increase roof surface temperatures by 30–50°F, accelerating material failure.
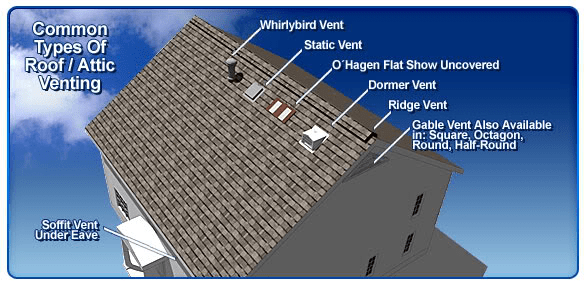
Types of Roof Vents Used on Storm Houses
Different vents serve different purposes. Choosing the right combination is critical.
1. Ridge Vents
Installed along the roof peak, ridge vents provide continuous airflow.
Pros
- Even ventilation
- Low-profile (wind-resistant)
- Ideal for storm-rated roofs
Cons
- Requires proper soffit intake
2. Box (Static) Roof Vents
Small vents placed near the roof ridge.
Pros
- Affordable
- Easy to install
Cons
- Less efficient than ridge vents
- Requires multiple units
3. Turbine Vents
Wind-powered vents that spin to pull air out.
Pros
- Active ventilation
- Effective in windy areas
Cons
- Moving parts can fail in storms
4. Soffit Vents (Intake)
Installed under roof eaves to allow air intake.
Pros
- Essential for balanced airflow
- Protected from direct rain
Cons
- Can clog if not maintained
Roof Vents and Storm Pressure: Why They Matter
One lesser-known answer to what is the purpose of vent on storm house roof relates to pressure equalization.
During Severe Storms:
- External air pressure drops rapidly
- Trapped hot air expands inside the attic
- Pressure imbalance can lift roof decking
Proper roof ventilation allows pressure to escape safely, reducing the risk of roof blow-off.
Heat Control: A Major Benefit of Roof Vents
In hot climates, storm-resistant homes often face intense solar exposure.
Benefits of Heat Reduction
- Lowers attic temperature by 20–30°F
- Reduces HVAC workload
- Cuts cooling energy costs by 10–15%
- Prevents shingle cracking and blistering
This makes roof vents a cost-saving feature—not just a protective one.
Moisture Control and Mold Prevention
Storms bring heavy rain and high humidity. Without vents, moisture becomes trapped.
What Happens Without Ventilation?
- Condensation forms on rafters
- Insulation absorbs moisture
- Mold spores spread
- Indoor air quality declines
Roof vents allow moist air to escape before it causes long-term damage.
Roof Ventilation vs No Ventilation (Comparison)
| Feature | With Roof Vents | Without Roof Vents |
|---|---|---|
| Attic Temperature | Lower & stable | Extremely high |
| Moisture Control | Effective | Poor |
| Roof Lifespan | Longer | Shortened |
| Storm Resistance | Stronger | Weaker |
| Energy Costs | Lower | Higher |
Are Roof Vents Safe During Heavy Rain and Hurricanes?
Yes—when properly designed.
Modern storm-rated roof vents:
- Include internal baffles
- Prevent wind-driven rain entry
- Meet building code requirements
Improperly installed vents, however, can leak. Installation quality is just as important as vent type.
Step-by-Step: How Roof Vents Are Installed on Storm Houses
While professional installation is recommended, understanding the process builds confidence.
Basic Installation Overview
- Measure attic ventilation needs (net free vent area)
- Cut vent openings at designated locations
- Install flashing and waterproof membranes
- Secure vent with corrosion-resistant fasteners
- Seal edges with weather-rated sealant
- Test for airflow and leaks
Typical installation time: 2–4 hours per vent, depending on roof type.
How Many Roof Vents Does a Storm House Need?
The standard guideline is:
1 square foot of ventilation per 150 square feet of attic space
This is split evenly between intake and exhaust vents.
Example:
- Attic size: 1,500 sq ft
- Required ventilation: 10 sq ft
- Intake: 5 sq ft
- Exhaust: 5 sq ft
Balanced ventilation is crucial for storm performance.
Common Mistakes Homeowners Make with Roof Vents
Avoid these costly errors:
- Installing exhaust vents without intake vents
- Mixing incompatible vent types
- Blocking soffit vents with insulation
- Skipping storm-rated vent covers
Each mistake reduces the effectiveness of the entire system.
Building Codes and Roof Vent Requirements
Most U.S. building codes require attic ventilation for residential homes, especially in storm-prone regions. These standards are based on long-standing construction science.
For general background on how roofs and ventilation systems function, you can reference:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Roof
(This link is provided for educational context only.)
FAQ: What Is The Purpose Of Vent On Storm House Roof?
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is the main purpose of roof vents on storm houses?
A: To release heat, control moisture, and stabilize pressure during storms.
Q2: Can roof vents cause leaks during heavy rain?
A: Not if they are storm-rated and properly installed.
Q3: Are ridge vents better than box vents for storm homes?
A: Yes. Ridge vents provide more even airflow and better wind resistance.
Q4: Do roof vents help during hurricanes?
A: Yes. They help equalize pressure and reduce roof uplift risk.
Q5: Can I add roof vents to an existing storm house?
A: Yes, but a professional assessment is recommended.
Conclusion: A Small Feature with Big Protection Benefits
So, what is the purpose of vent on storm house roof? Roof vents are essential for managing heat, moisture, and pressure—three major threats during severe weather. They protect your roof structure, lower energy costs, and improve indoor comfort year-round.
If this guide helped you understand roof ventilation better, share it on social media so other homeowners can protect their homes more effectively.



Leave a Reply